In the dynamic landscape of manufacturing, Production Planning and Control (PPC) emerge as crucial processes ensuring efficiency and smooth operations. Production Planning involves setting objectives for optimal manufacturing, while Control oversees execution to meet those goals. The twin pillars of PPC aim to reduce costs, enhance delivery timelines, and streamline processes. From initial planning to the final follow-up, each step plays a pivotal role. Various types of planning, such as Master Production Scheduling and Materials Requirement Planning, along with tools like Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), contribute to the overall success of PPC. This guide will delve into the significance, steps, and tools involved, shedding light on how PPC remains indispensable in today’s manufacturing realm.
Production Planning
Production Planning is like creating a roadmap for making things go smoothly. Imagine you’re baking cookies. Before you start mixing ingredients, you plan how many cookies, what elements, and when to bake. In manufacturing, it’s the same but on a bigger scale. It’s about figuring out what to make, how much, and when. This helps avoid chaos and makes everything work like a well-oiled machine. The goal is to be smart about it—use resources wisely, keep costs down, and make sure things are ready when needed. So, production planning is like the secret sauce that makes sure everything comes together just right.
Production Control
Think of Production Control as the superhero making sure everything stays on track in the manufacturing world. Once you’ve planned what to make and how much (like planning a party guest list), Production Control kicks in. It’s about overseeing the actual making—making sure everyone and everything is where it needs to be, doing what they’re supposed to. Imagine it’s a dance, and Production Control is the choreographer, making sure everyone hits their moves at the right time. This superhero helps keep costs in check, makes certain things are running smoothly, and ensures that the final product is top-notch. In a nutshell, Production Control is the behind-the-scenes magic making sure the show goes on without a hitch.
What are the Objectives of Production Planning and Control?
The following specific objectives:
- Optimizing Resource Utilization: Make the best use of available resources, including people, machines, and materials, to meet production demand efficiently.
- Efficient Scheduling: Develop a schedule that ensures smooth and effective production processes, minimizing downtime and delays.
- Timely Resource Availability: Ensure that resources are ready and available when needed, preventing bottlenecks and disruptions in the production flow.
- Optimal Inventory Levels: Keep inventory at optimal levels, avoiding overstock or shortages and reducing carrying costs.
- Increased Productivity: Enhance the productivity of internal resources, such as workers, work centres, and machinery, to maximize output.
- Customer Satisfaction: Improve customer satisfaction by delivering products on time and meeting quality standards.
- Appropriate Task Assignment: Ensure the right personnel are assigned to specific processes, utilizing skills effectively.
- Interdepartmental Coordination: Coordinate with other departments, including sales, customer service, and purchasing, to align production activities with overall business goals.
In essence, production planning and control form the backbone of manufacturing, orchestrating a seamless flow of operations to meet demand, utilize resources efficiently, and deliver high-quality products on time.
Steps in Production Planning and Control
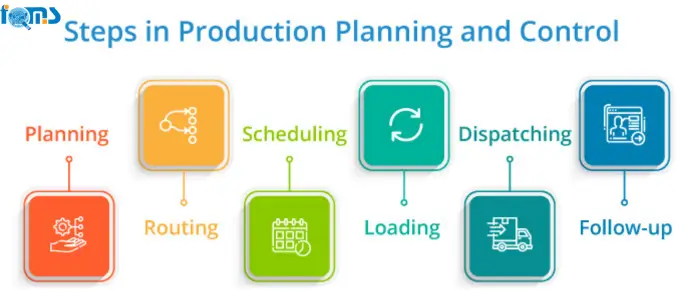
1. Planning
Planning sets the stage, deciding what, how, and by whom things will be produced. It’s like creating a blueprint, considering factors like order quantities, delivery dates, and product specifications to keep the production process streamlined.
2. Routing
Routing guides the flow of raw materials through the factory, showing the path from start to finish. It’s the GPS of production, detailing quantity, quality, and operations. By coordinating every step, it ensures efficient resource utilization.
3. Scheduling
Scheduling focuses on the “when” of operations, aiming to make the most of available time. It involves different schedules, such as Master Schedule and Daily Schedule, to manage time effectively and complete operations on schedule.
4. Loading
Loading checks the workload on machines or workers. If there’s capacity, more work is added; if overloaded, measures like overtime or subcontracting are considered to prevent bottlenecks.
5. Dispatching
Dispatching is the release of orders and instructions, ensuring everything is ready for employees to start their tasks. It includes issuing materials, orders, and maintaining records for a smooth workflow.
6. Follow-up
Follow-up, or expediting, identifies issues in the production process. It compares actual performance with expectations, addressing problems like delays or defects. It’s about finding the root cause and making adjustments to keep the production on track. It’s the checkpoint ensuring everything goes as planned.
Types of Production Planning
Master Production Schedule
A Master Production Schedule is like a detailed plan for a grand event. It outlines when, how much, and what products will be made, ensuring timely delivery and avoiding excess stock.
Materials Requirement Planning
Materials Requirement Planning is the guardian of raw materials. It ensures they’re always on hand, keeps stock at the minimum, and helps control inventory, making purchasing activities a breeze.
Capacity Planning
Capacity Planning is the matchmaker between what customers want and what the organization can produce. It finds the sweet spot, balancing expenses, resources, and the ebb and flow of demand.
Workflow Planning
Workflow Planning is like choreographing a dance. It plans the sequence of operations during production, allowing tracking of tasks and responsibilities. In simpler terms, it’s the tool that keeps an eye on each task’s progress.
Production Planning Tools
In the world of making things, there are some handy tools to keep everything in order, just like having the right tools in a kitchen.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
Think of ERP as the superhero organizer. It helps manage everything from planning to delivery, making sure all parts of production are in sync.
Benefits of ERP in Production Planning
ERP brings big perks. It makes planning smoother, reduces errors, and keeps everyone on the same page. It’s like a GPS for the entire production journey.
So, just like a chef needs the right tools in the kitchen, production planning needs ERP to make everything run like a well-oiled machine.
Conclusion
In the fascinating world of making things, Production Planning and Control (PPC) emerge as the architects ensure everything falls into place. It’s like orchestrating a grand event, where planning sets the stage, and Control provides a flawless performance. The objectives—efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and timely delivery—are met through steps like planning, routing, and scheduling. Types such as Master Production Schedule and Materials Requirement Planning act as the blueprints, while tools like Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) serve as the trusty sidekicks, making the entire journey smoother. Picture it like a well-coordinated dance, where each step, from planning to using the right tools, contributes to the harmonious success of production. So, in the realm of making things happen, PPC stands tall, ensuring the show goes on without a hitch.


![POS system [software and machine ]Details-FQMSYS](https://fqmsys.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/Conventional-Meta-Analysis.webp)