Retail business is more complicated than ever. Inventory management is a headache, customers expect seamless experiences and the competition is fierce. Retail Business ERP is essential for all retailers.
This guide will show you how Retail Business ERP functions, what it offers, and how you can choose the right solution for your business, whether you sell online or in store.
What is ERP for Retail?
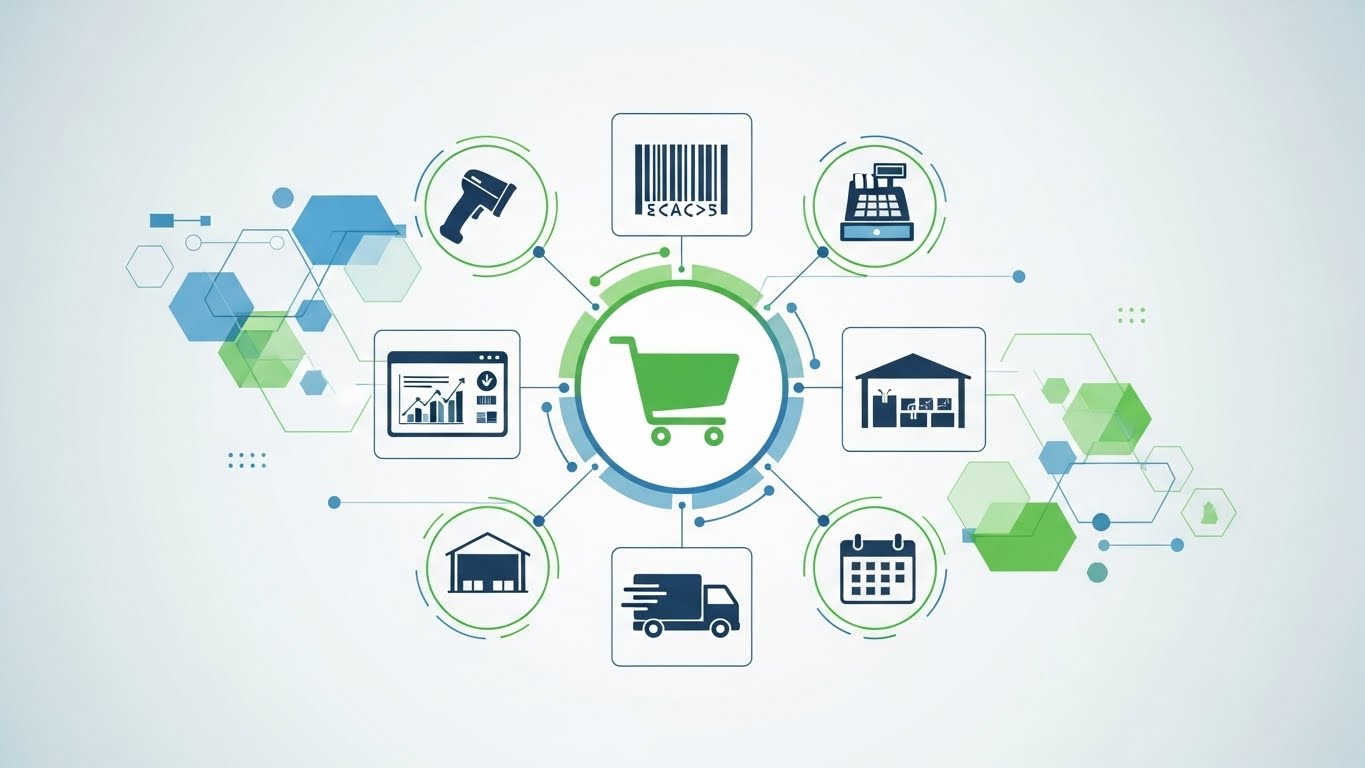
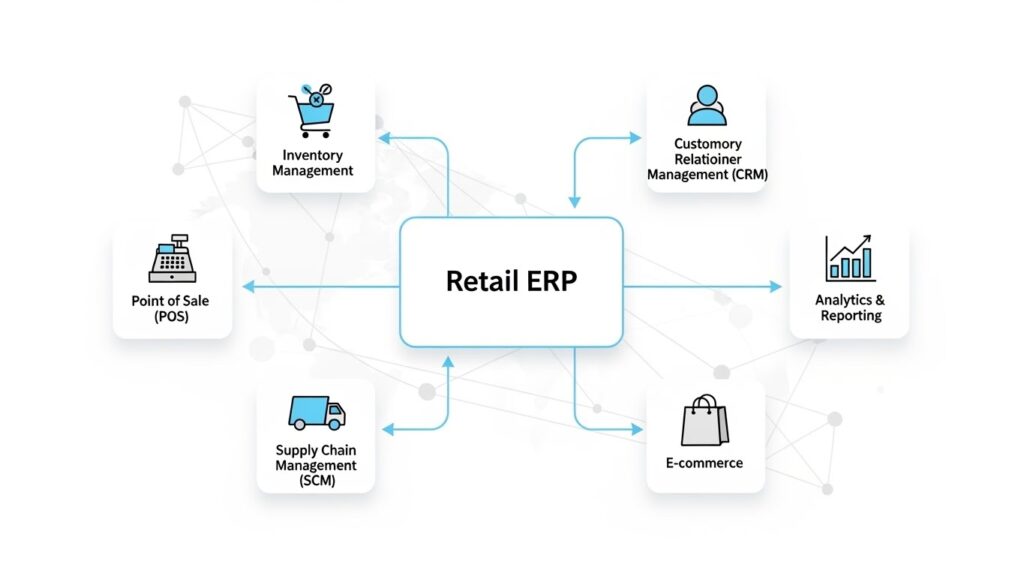
ERP is a retail software system which helps retailers to manage their key operations, such as inventory management, sales and finance, customer service and supply chain, from a single platform.
Imagine it as a command centre for your business. Retail ERP integrates spreadsheets, POS Software, and multiple Apps into a single dashboard.
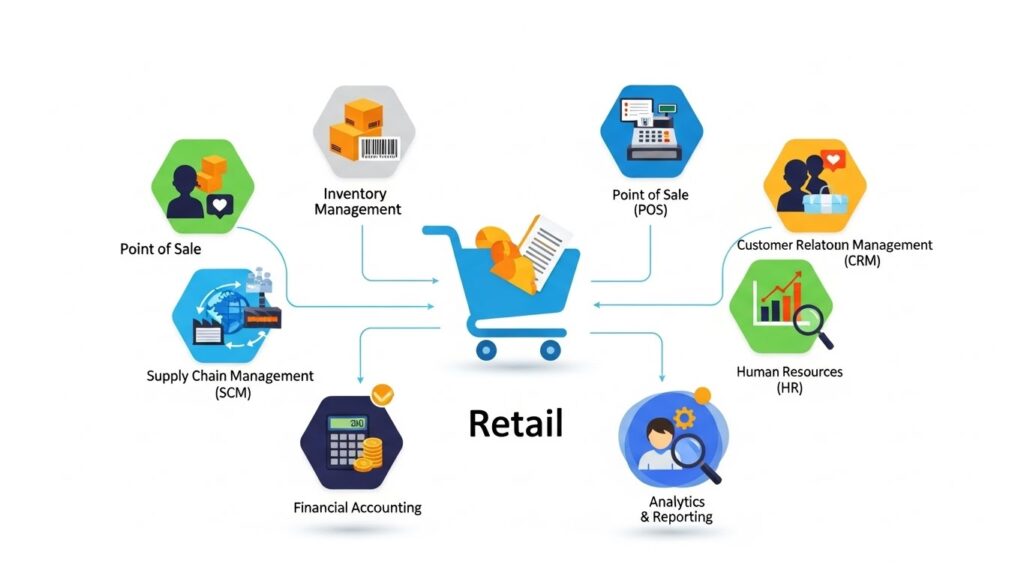
Key Features Include:
- Inventory management
- Point-of-sale (POS)
- Customer relationship management (CRM)
- Supply chain management
- Financial accounting
Anecdote A clothing store in Lahore would oversell the most popular items and let slow-moving inventory pile up. The owner of a small clothing store in Lahore was able to see the inventory levels in real time, and reduce waste after implementing an ERP. This led to a 20% profit increase in only three months.
Which ERP does TCS use?
Tata Consultancy Services, a global provider of IT services, implements solutions such as and SAP ERP to support large-scale operations. Other customized ERPs are also used, depending on the client’s requirements.
The importance of ERP solutions for retail businesses can be learned from TCS.
Does SAP have a CRM component or an ERP component?
Is it a CRM, or an ERP? Both.
- The SAP ERP system is a comprehensive enterprise resource planning software that manages inventory and finance. It also handles supply chain management.
- SAPCR SAP CRM focuses on customer relations and sales processes.
SAP ERP is a great tool for retailers because it connects all the functions and helps to build better experiences for customers.
Is B2C ERP the same as B2B?
ERP systems can serve both B2B (business-to-business) and B2C (business-to-consumer) models.
- B2B: Manages wholesale orders, bulk orders and supplier relationships.
- B2C: Focuses retail sales, online shops, customer engagement and point of sale integration.
Modern retail ERPs can handle B2B as well as B2C scenarios. This makes them perfect for retailers looking to expand their business into other channels.
How Retail ERP Works
Imagine your retail business is a wheel. Each spoke represents a different department: sales, inventory, finance, human resources, ecommerce, and customer services. ERP connects the spokes, so that information can flow instantly.
As an example:
- automatically updates inventory when a product is sold at the POS.
- Supplier deliveries update costs in finance.
- Orders online are synced with stock levels in real time.
- Instantly, managers can get dashboards of performance.
This -connected workflow reduces errors and helps retailers to make smarter, faster decisions.
A Step-by-Step guide to Implementing ERP in Retail
Step 1: Identify Business Needs
Question yourself:
- Do I own multiple stores?
- Can I sell both online and off-line?
- Do I require automatic stock tracking?
- Do I require integrated accounting and CRM systems?
Step 2: Research ERP Systems
Popular options include
Choose one that suits your budget, store size and technical requirements.
Step 4: Request a demo
Watch the system in action
- Test dashboards
- Check POS integration
- Usefulness of the product is evaluated
- Test mobile apps
Step 4: Implement in Phases
Start with the core modules
- Inventory
- POS
- Financial Services
Later, you can expand to supply chain, e-commerce and HR.
Step 5: Train Your Team
To avoid errors, staff must be able to use the system correctly.
Step 6: Monitor
Analyze reports, track KPIs and refine processes. When you adapt ERP continuously, it is at its most effective.
Benefits of ERP in Retail Business
- Real Time Inventory Visibility No Stockouts or Overstocks.
- Reduced Operating Costs– Automation reduces errors and labor.
- Improved Customer Experience Fast billing, loyalty programmes, and personalized offers.
- Data Driven Decisions Use analytics to identify opportunities for growth.
- Scalability– ERP grows with your business.
Common Retail challenges solved by ERP
- Inventory forecasting – Overstocking, stockouts and inventory forecasting
- Automated finance module
- Dashboards and reports – Uncertain sales performance
- Poor CRM and loyalty integration
Conclusion: Why Retail Businesses Should Invest In ERP
A retail ERP system is more than just software. It’s an instrument for growth.
This software streamlines operations and improves customer satisfaction. It also increases profitability.
No matter if you run a small boutique or a large chain of stores, ERP will help you work smarter and not harder. ERP will help your retail business grow tomorrow if you invest today.



